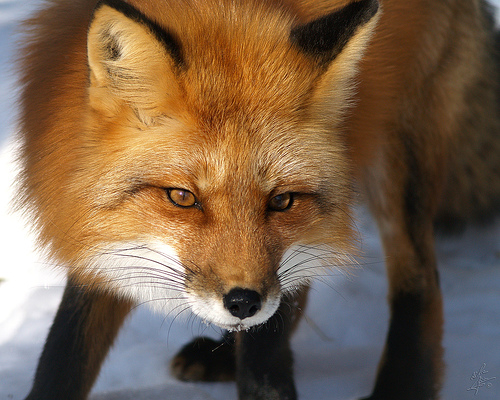
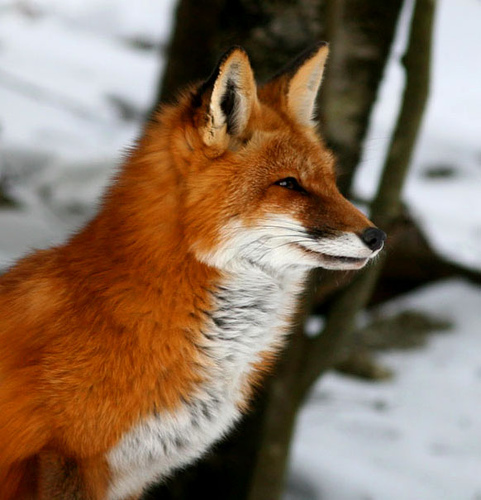
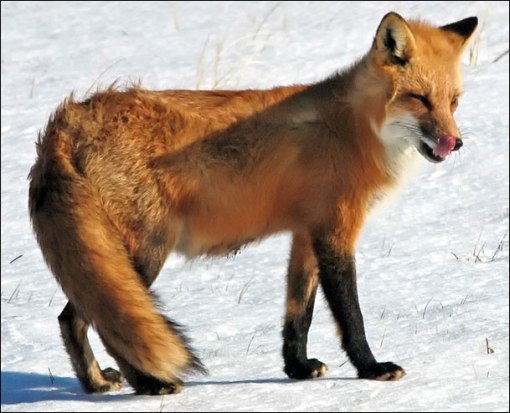
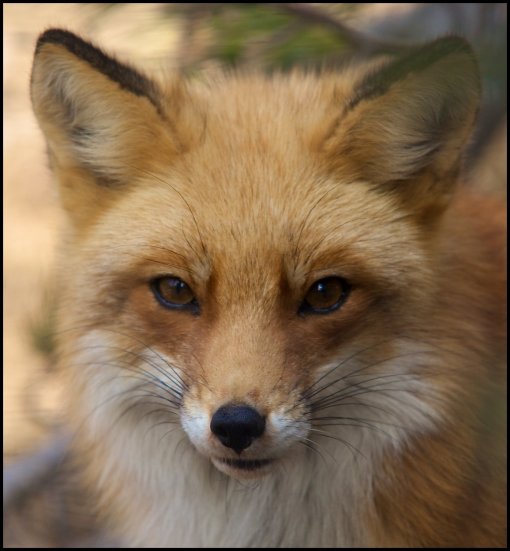
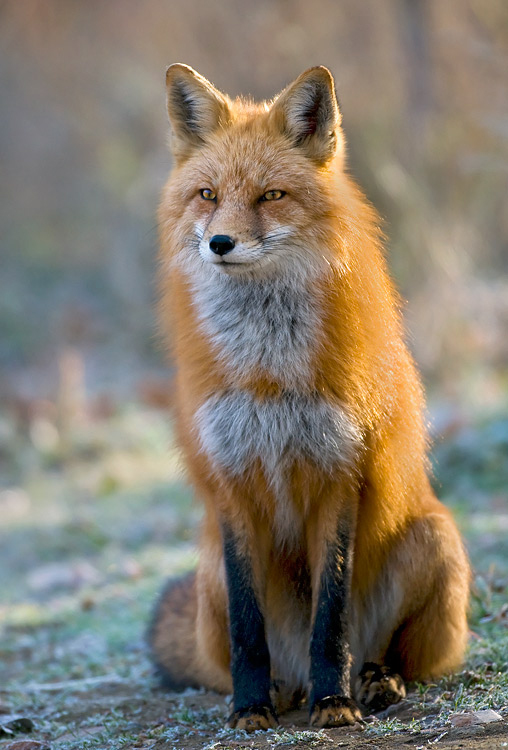
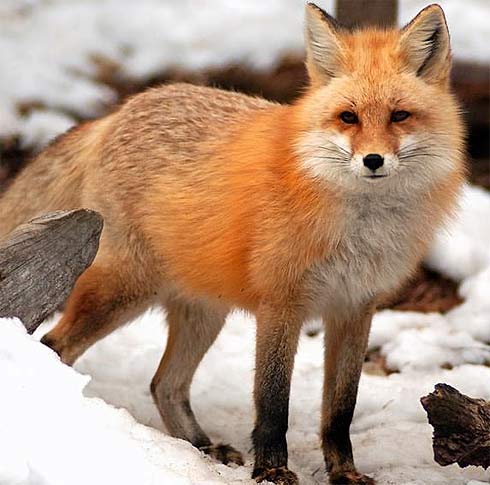
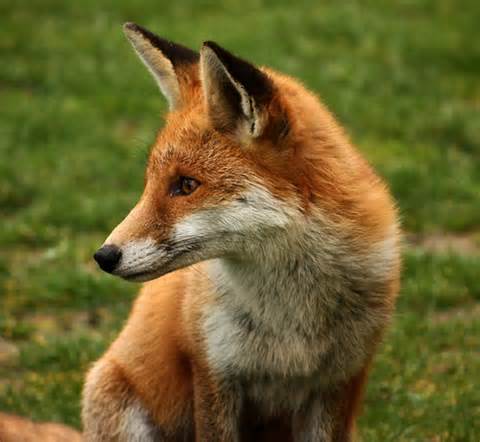
Red foxes live around the world in many diverse habitats including forests, grasslands, mountains, and deserts. They also adapt well to human environments such as farms, suburban areas, and even large communities. The red fox’s resourcefulness has earned it a legendary reputation for intelligence and cunning.
The small, slender bodies of red foxes are designed for speed and agility. In proportion to other canid species, red foxes have longer legs and smaller stomachs — adaptations that allow the animal to run nearly 30 miles per hour. A smaller stomach means they need to eat more often, and red foxes opportunistically eat a wide variety of foods as they traverses their home range at night, such as insects, fruits, earthworms, and scraps left by humans. Although they also hunt during the day, red foxes have very acute senses to help them succeed as nocturnal predators. Their eyes are designed to work well in low light conditions, and they maneuver their erect triangular ears to locate the faint rustling noises of rodents. When a mouse is detected, red foxes stand alert and motionless, using their ears and eyes to pinpoint the location of the rodent. Then they launch themselves into the air at a 45-degree angle, and land on the mouse, pinning it to the ground.
Although Red foxes are solitary hunters who feed on rodents, they also feed on rabbits, birds, and other small game—but their diet can be as flexible as their home habitat. Foxes will eat fruit and vegetables, fish, frogs, and even worms. If living among humans, foxes will opportunistically dine on garbage and pet food. >>> Read more from our earlier blog The red fox (Vulpes vulpes).
***
Like a cat’s, the fox’s thick tail aids its balance, but it has other uses as well. A fox uses its tail (or “brush”) as a warm cover in cold weather and as a signal flag to communicate with other foxes.
Foxes also signal each other by making scent posts—urinating on trees or rocks to announce their presence.
In winter, foxes meet to mate. The vixen (female) typically gives birth to a litter of 2 to 12 pups. At birth, red foxes are actually brown or gray. A new red coat usually grows in by the end of the first month, but some red foxes are golden, reddish-brown, silver, or even black. Both parents care for their young through the summer before they are able to strike out on their own in the fall.
Red foxes are hunted for sport, though not extensively, and are sometimes killed as destructive pests or frequent carriers of rabies
-
Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes)
- Type: Mammal
- Family: Canidae
- Habitat: Highly variable. Edge forests, deserts, tundra, cities, and suburban areas
- Location: Most of the Northern Hemisphere and Australia
- Diet: Rodents, birds, insects, carrion and fruit
- Average lifespan in the wild: 3 years in the wild; 10-12 years in captivity
- Size: Head and body 18-35.4 in (45.5-90 cm); tail 11.8-21.8 in (30-55.5 cm)
- Weight: 6.6-30.8 lbs (3-14 kg)
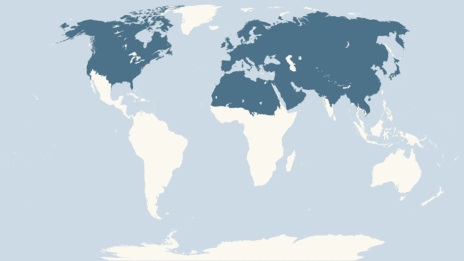
Red foxes have excellent hearing. They can hear low-frequency sounds and rodents digging underground.World wide Distribution map of Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes).As you can see from the above map, Red foxes have the largest distribution of any canid species. They can be found in almost the entire northern hemisphere, in part because they have such a diverse diet. As a species, red foxes have adapted well to human expansion. They thrive in urban areas, and have benefited from the human conversion of forest into agricultural lands. Red foxes are often seen as a threat to poultry and young livestock, even though they usually prey only on weak and sick animals. Though many farmers consider them pests, red foxes play a major role in controlling populations of crop-threatening animals like rabbits and rodents.
Did you know: Red fox predators are eagles, coyotes, gray wolves, bears, mountain lions, and humans, who have been hunting red foxes since the 4th century BC.
Subspecies
As Red Foxes have such a wide range, they have many subspecies. Below are a list of subspecies and their locations:
Vulpes vulpes abietorum – Western Canada
Vulpes vulpes aeygptica – Egypt
Vulpes vulpes alascensis – Alaska
Vulpes vulpes alpherakyi – Turkestan
Vulpes vulpes alticola
Vulpes vulpes anatolica – Asia
Vulpes vulpes arabica – Muscat
Vulpes vulpes atlantica
Vulpes vulpes barbara – North West Africa
Vulpes vulpes beringiana – North East Siberia
Vulpes vulpes cascadensis – NW coast of USA
Vulpes vulpes caucasica – Caucasian Mount. area
Vulpes vulpes crucigera – Germany
Vulpes vulpes daurica
Vulpes vulpes diluta
Vulpes vulpes dolichocrania – Russia
Vulpes vulpes dorsalis
Vulpes vulpes flavescens – North Iran
Vulpes vulpes fulva – Eastern USA
Vulpes vulpes fulvus
Vulpes vulpes griffithi – Afghanistan
Vulpes vulpes harrimani – Alaska
Vulpes vulpes hoole – South China
Vulpes vulpes ichnusae – Sardinia
Vulpes vulpes induta – Cyprus
Vulpes vulpes jakutensis – Yakutsk
Vulpes vulpes japonica – Japan
Vulpes vulpes karagan – Khirgizia
Vulpes vulpes kenaiensis – Alaska
Vulpes vulpes krimeamontana – Crimea
Vulpes vulpes kurdistanica
Vulpes vulpes macroura – Rocky Mts, USA
Vulpes vulpes montana – Himalayas
Vulpes vulpes necator – Western USA
Vulpes vulpes ochroxanta
Vulpes vulpes palaestina – Palestine
Vulpes vulpes peculiosa – Korea
Vulpes vulpes pusilla – India
Vulpes vulpes regalis
Vulpes vulpes rubricosa – Canada
Vulpes vulpes schrencki – Sakhalin
Vulpes vulpes septentrionalis
Vulpes vulpes silacea – Spain
Vulpes vulpes splendidissima – Kurile Is.
Vulpes vulpes stepensis
Vulpes vulpes topolica
Vulpes vulpes tschiliensis – North East China
Vulpes vulpes vulpecula
Vulpes vulpes vulpes
Vulpes vulpes waddelli – TibetPrized Pelts
Before the collapse of the fur trade, the red fox’s fur was highly valued, and the red fox was heavily hunted. The fall of the fur trade and innovative fencing techniques used by farmers to protect their poultry have excluded the need to hunt and kill the red fox. Though the canine’s population is improving throughout the United States, it still faces a struggle as it competes with coyotes for habitat.
***